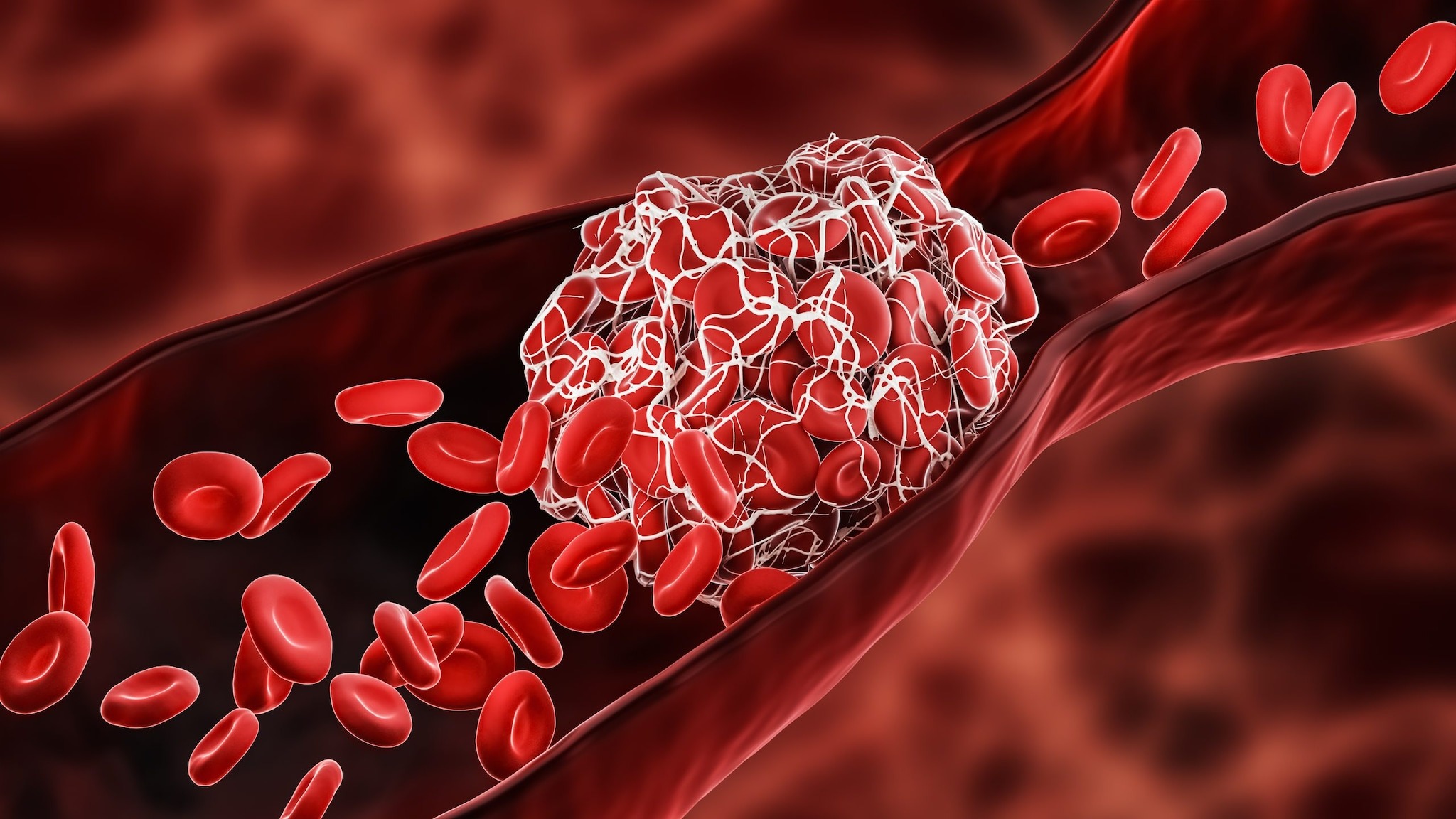
For the body to stay healthy and function properly, continuous blood circulation is essential. Blood clotting plays a crucial role in this process. It helps prevent excessive bleeding in case of injuries.
Health experts explain that clotting is a natural defense mechanism that stops bleeding with the help of platelets and specific proteins. However, when unnecessary blood clots form in veins or arteries, they can lead to severe health complications.
Risks of Unnecessary Blood Clots
Clots forming in arteries can contribute to life-threatening conditions such as heart attacks. This is why everyone needs to be aware of their clotting risks. Understanding why blood clots occur and how to prevent them is essential for maintaining good health.
Blood Clotting Disorder (BCD) and Its Causes
Blood Clotting Disorder (BCD), also known as thrombophilia, causes blood to clot too quickly. While clotting is necessary to prevent excessive bleeding, abnormal clotting can be dangerous. Several factors increase the risk of blood clotting, including:
- Cancer treatments – Medications for cancer may elevate the risk of clot formation.
- Obesity and pregnancy – Both conditions can increase the likelihood of developing blood clots.
- Hormonal medications – Excessive use of birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy may contribute to clot formation.
- Physical inactivity – A sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of clotting-related complications.
Potential Complications of Blood Clots
When blood clots develop in the wrong places, they can cause severe health issues, such as:
- Brain clots – These can block oxygen supply, leading to paralysis or strokes.
- Heart clots – If blood clots form in the arteries of the heart, they can cause circulation problems and heart attacks.
Signs of Blood Clot Formation
Recognizing the symptoms of blood clots is crucial for early intervention. Common warning signs include:
- Swelling in the arms or legs – Usually occurring on one side of the body.
- Skin discoloration – The affected area may turn blue or darker due to restricted blood flow.
- Sharp, unexplained pain – Often occurring in the arms or legs.
- Breathing difficulties and chest pain – Indicating a possible clot in the lungs.
- Dizziness or fainting – If the clot reaches the brain, it can impair consciousness.
- Speech difficulties – A possible sign of a stroke caused by a brain clot.
Preventing Blood Clots
To reduce the risk of dangerous blood clots, experts recommend the following measures:
- Seek medical advice – If you suspect a clotting issue, consult a doctor immediately.
- Use prescribed medications – Certain drugs can help manage clotting disorders.
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle – Regular physical activity and a balanced diet can help prevent excessive clotting.
- Stay hydrated – Drinking plenty of water improves circulation and reduces clotting risks.
- Avoid prolonged immobility – Sitting or lying down for extended periods can increase the risk of clot formation.

 Share
Share






